Originality is more than a moral expectation; it is a requirement for credibility and success. Writers across disciplines are increasingly turning to plagiarism detection tools not just as a safety net, but as a way to refine their writing, improve citation practices, and cultivate a deeper understanding of proper attribution. Plagiarism tools serve a dual purpose: they identify potentially unoriginal content and offer insight into how to better integrate sources, thereby enhancing both the quality and ethical integrity of one’s work.
The Prevalence of Plagiarism and Citation Issues
Despite widespread awareness of academic integrity, studies indicate that issues with plagiarism and improper citation remain common. Research in higher education suggests that approximately 30 percent of student submissions contain significant citation or attribution errors, ranging from missing references to paraphrasing without acknowledgment. In professional writing, surveys indicate that 10 to 15 percent of content across blogs, whitepapers, and online articles shows evidence of insufficient attribution. These numbers highlight the importance of proactive tools that guide authors in identifying potential overlaps and improving citation practices before submission or publication.
How Plagiarism Tools Support Writing Improvement
Plagiarism detection tools, such as Turnitin, PlagCheck, and PlagiarismSearch, are designed not only to flag unoriginal text but also to provide contextual feedback. By highlighting text that closely resembles existing sources, these tools allow authors to evaluate whether paraphrasing is adequate or if proper citations are missing. In addition, many modern platforms offer suggestions for rewording or prompt authors to include the appropriate references. This iterative feedback process helps writers develop stronger, more precise academic and professional writing skills over time.
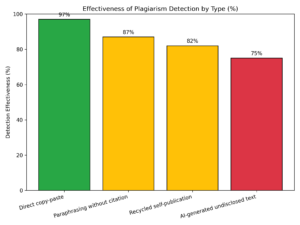
Statistics on Tool Effectiveness
Modern plagiarism detection platforms have achieved remarkable effectiveness. Evaluations show that over 95 percent of direct text matches are accurately flagged, while paraphrased or slightly modified content can be detected in roughly 85 percent of cases. Notably, integration of AI-powered semantic analysis has improved detection of more subtle citation errors, such as improper paraphrasing or rewording without attribution. This allows authors to proactively correct mistakes and strengthen their citation practices before content reaches editors, instructors, or publishers.
Effectiveness of Plagiarism Detection Tools
The chart below illustrates the estimated prevalence of different types of plagiarism and the corresponding effectiveness of modern plagiarism detection tools.
Improving Citation Practices Through Detection
Beyond identifying unoriginal text, plagiarism tools play a critical role in teaching and reinforcing proper citation habits. Authors can learn to differentiate between common knowledge, direct quotations, and paraphrased content, which is crucial for ethical writing. Research indicates that students who use plagiarism detection software as part of their writing workflow are 20–30 percent less likely to submit work with citation errors, demonstrating the direct impact of these tools on writing quality. By repeatedly reviewing flagged passages and addressing feedback, writers internalize proper attribution standards, reducing the likelihood of future errors.
AI-Enhanced Writing and Plagiarism Detection
The rise of AI-assisted writing has added new dimensions to plagiarism and citation concerns. Generative AI tools can help draft text, summarize research, or suggest phrasing, but improper use may inadvertently lead to unoriginal content. Many modern plagiarism detection platforms now include AI-recognition features, identifying text that may be AI-generated and highlighting areas where citations or attribution are required. These systems help authors maintain ethical standards while taking advantage of technological assistance, ensuring that AI-supported writing remains fully transparent and academically sound.
Case Study: Academic and Professional Use
In academic settings, integration of plagiarism tools into writing curricula has demonstrated measurable improvements in student outcomes. Studies have shown that students who consistently used detection tools before submitting assignments reduced citation errors by up to 25 percent, while overall text originality scores improved by 15–20 percent. Similarly, professional writers using plagiarism checkers report fewer editorial revisions related to attribution and improved client satisfaction due to higher content integrity. These examples underscore how plagiarism tools act not just as preventative measures, but as instruments for developing stronger writing habits and ethical awareness.
Challenges and Considerations
While plagiarism detection tools are highly effective, they are not infallible. False positives can occur, particularly with commonly used phrases, technical terms, or properly quoted material that closely matches source text. Authors must interpret reports critically, understanding that the purpose of the tool is guidance rather than definitive judgment. Additionally, AI recognition features may flag stylistic similarities that are not genuine plagiarism, requiring nuanced evaluation and editorial discretion.
Integrating Plagiarism Tools Into Your Workflow
For optimal results, writers are encouraged to integrate plagiarism detection into their writing workflow rather than treating it as a final check. Using tools iteratively during drafting allows authors to address citation issues, refine paraphrasing, and ensure originality as content develops. This approach not only reduces the risk of unintentional plagiarism but also fosters deeper engagement with source material, encouraging thoughtful synthesis and accurate attribution. Over time, the consistent use of plagiarism tools can transform writing habits, making ethical citation and original expression a natural part of the creative process.
Future Directions in Writing and Detection
As digital content creation evolves, plagiarism tools will increasingly incorporate AI-assisted feedback and real-time suggestions for citation and paraphrasing. Emerging technologies aim to provide authors with actionable insights during the writing process, rather than simply highlighting potential issues after submission. This proactive approach has the potential to redefine how writers learn and maintain ethical standards, supporting both creativity and integrity in a world where content is rapidly produced and widely shared.
Conclusion: Plagiarism Tools as a Writing Resource
Plagiarism detection tools have grown far beyond their original role as mere safeguards against misconduct. Today, they are essential resources for writers seeking to improve their skills, strengthen citation practices, and produce high-quality, ethically sound content. By combining automated feedback with critical interpretation, writers can learn to identify unoriginal text, correct citation errors, and develop long-term habits that support academic and professional integrity. In this way, plagiarism tools not only prevent ethical violations but actively contribute to the growth of better, more responsible writing.

